Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm(AAA)
Abdominal aortic aneurysm is a very common disease in which the lower portion of abdominal aorta is enlarged making a balloon like structure called aneurysm. Abdominal aortic aneurysm makes the aorta weak and bulging.The aorta is the main artery in human body which supplies blood to the abdomen, pelvis and legs. The aorta runs from your heart through the center of your chest and abdomen. Since, aorta is responsible for the distribution of oxygenated blood to all parts of your body, a ruptured aorta can cause internal bleeding and can be life threating.Usually, abdominal aortic aneurysm grows slowly making detection difficult. In some AAA cases, the wall never ruptures.Abdominal aortic aneurysm starts small but can expand over time.Some aneurysm expand quickly and some retain at their small sizeThe size and growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysm decides the treatment which varies from watchful waiting to an emergency surgery which can be risky.
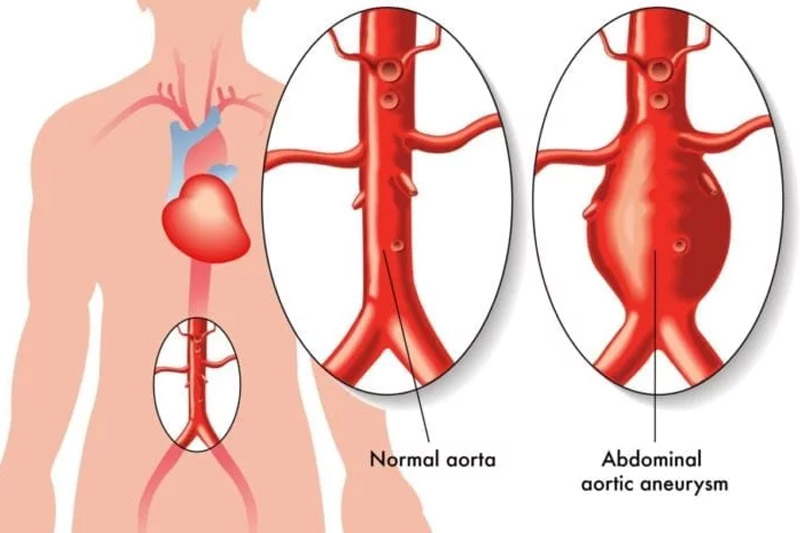
Symptoms and complications:- The abdominal aortic aneurysm disease can be with or without symptoms which makes diagnosis difficult. When an abdominal aortic aneurysm enlarges, people may feel
- A pulsating feeling near the navel.
- Constant pain in your abdomen or on the side of your abdomen.
- Back Pain
Rupturing in the wall of aorta(dissection) is the main complication associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm. It depends on the size of aneurysm, the larger the aneurysm, the greater the risk of rupturing. A ruptured aortic aneurysm may cause internal bleeding which can be life threatening.
Signs and symptoms that your aortic aneurysm has ruptured are:-
- Sudden severe abdomen or back pain spreading to the groin,buttocks and legs.
- Sweating.
- Dizziness.
- Clammy Skin.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Rapid heartrate.
- Shock.
- Low blood pressure
- Fast pulse
- Loss of consciousness
- Shortness of breath.
One major complication associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm is the risk of blood clots. Aortic aneurysm area can develop small blood clots which if breaks loose from the inside wall of aneurysm and blocks a blood vessel elsewhere in your body, it can cause pain or block the blood flow to the other body organs.
Causes:- a Although the cause of abdominal aortic aneurysm is unknown, some factors that can increase the problem are:-
- Smoking and Tobacco use:- Cigarette smoking and other forms of tobacco use may increase the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- High Blood Pressure:- High blood pressure also increases the risk of AAA.
- Gender:- Males are more prone to get an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- Genetic factors:- If a person belongs to a family which has a history of abdominal aortic aneurysm, the risk of getting the disease increases.
- Age:- People above 60 are more prone to develop abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- Atherosclerosis:- Atherosclerosis is the deposit of fat and other substances that may damage the lining of a blood vessel and increases the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm..
- Blood vessel diseases:- Blood vessel disease increases the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- Infection in the aorta (Vasculitis):- Inflammation and infection in aorta may cause AAA.
Tests and Diagnosis:- Abdominal aortic aneurysm often have no symptoms and are predicted during examination of other problems. Like, if you go for a routine checkup and your doctor finds a pulsating bulge in your abdomen. Abdominal aortic aneurysm are often found during medical tests, such as chest X-ray or ultrasound of the heart or abdomen, sometimes ordered for a different reason.When your doctor suspects about aortic aneurysm, further specialized tests are done to confirm it. The tests may include:-
- Abdominal Ultrasound:- This test may help to diagnose the abdominal aortic aneurysm. It is a painless exam in which an instrument called transducer sends images to a computer screen that a technician monitors to check for any potential aneurysm.
- Computerized Tomography(CT) Scan:- This painless test can provide your doctor with clear images of your aorta and displays them on a computer monitor through which he can diagnose the illness.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):- MRI is again a painless test that provides the clear images of your aorta and finds if you have an aneurysm.
- Treatment and Drugs:- Treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm varies according to the size and growth of aneurysm.
- Small Aneurysm:- In case, if you have an aneurysm of about 4 cm or 1.6 inches or less than that, your doctor may believe in observation approach instead of surgery. Surgery is not needed for small aneurysm. The doctor monitors your aneurysm with ultrasounds at regular intervals, like every 6 to 12 months and you have to report immediately if you start having abdominal tenderness or back pain which can be a potential sign of dissect.
- Medium Aneurysm:- A medium size aneurysm is around 1.6 inches to 2.1 inches.(4 to 5.3 cm). In this case, it is difficult to decide whether you should go for surgery or use observation method. You will have to discuss about the risks and benefits of surgery versus waiting approach with your doctor and then take decision. If you select waiting and observation method, you will need to go for regular tests every 6 to 12 months and moniter your aneurysm carefully.
- Large, fast growing or leaking aneurysm:- You will probably need surgery in case if you an aneurysm larger than 2.2 inches or 5.6 cm. or the aneurysm is growing fast(grows more than 0.5 cm every six month).In addition, a leaking, tender or painful aneurysm needs treatment.
There are two types of surgery for aneurysm:-
- Open Abdomen Surgery:- An open abdomen surgery is done to cure an abdominal aortic aneurysm. It involves removing the ruptured section of the aorta and replacing it with a synthetic tube (graft) which is sewn in to place through an open abdominal method. This surgery usually takes a month or more to recover
- Endovascular Surgery:- Endovascular surgery is used to repair an aneurysm. Doctors attach a synthetic graft to the end of a thin tube (catheter)which is inserted through an artery in your leg and threaded up in to your aorta. The graft - a woven tube covered by a metal mesh support - is placed at the site of the aneurysm and fastened in place with small hooks or pins.The graft reinforces the weakened section of the aorta to prevent rupture of the aneurysm. The recovery time is shorter than open abdomen surgery but follow up appointments are more frequent because endovascular grafts can leak.
The treatment of aneurysm varies according to different factors like location of the aneurysm, your age, kidney function etc and other conditions that can increase the risk of surgery or repair.
Prevention: You can prevent the disease by following a healthy life style and keep your blood vessel as healthy as possible. Follow some easy steps listed below:-
- Eat healthy and reduce cholesterol and fat in your diet.
- Do regular exercise.
- Keep your blood pressure under control.
- Quit smoking and chewing tobacco.
If you have any risk factor for aortic aneurysm like age, high blood pressure, smoking habit or anything that increases the risk of getting abdominal aortic aneurysm, you must consult your doctor and take some additional measures to reduce the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm.