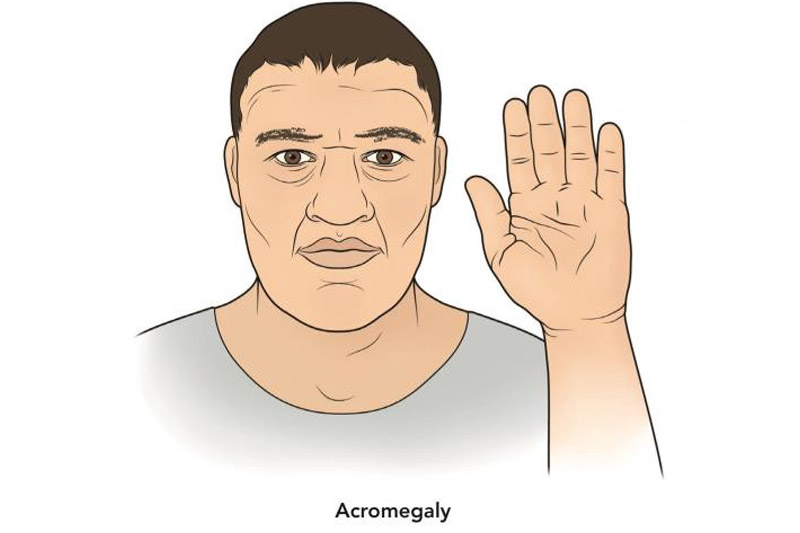
Acromegaly
‘ACRO’ means extremity and ‘MEGALY’ means enlargement. Acromegaly is relatively a rare disorder in adults which causes hypersecretion of the anterior lobe of the pituitary hormone called the Growth hormone (somatotropin) after the ossification is complete. It causes enlargement of the extremities like hands, face, feet. It is important to differentiate this from Gigantism which is also called by excess Growth hormone which occurs mainly in children before the ossification is completed.
CAUSE:
To understand the pathophysiology first let’s see how and from where growth hormone is secreted?
Hypothalamus secretes GH –Releasing Hormone (EVERY COUPLE OF HOURS). Its secretion can be increased during –
- Low blood glucose levels
- Lack of food
- Increased exercise
- Increased stress-trauma
- Increased sleep
The GH-Releasing hormone then goes into the hypophyseal portal system and binds to somatotropin cells and in response, they release growth hormone.
- Direct effects of growth hormone: Tissues where GH stimulates cellular metabolism causes organ growth by acting on:
- LIVER – by causing more glucose to release into the blood.
- MUSCLES – retains nitrogen which in turn causes more muscle growth.
- BONES- osteoblasts are stimulated which causes bone thickening
- It also causes increased insulin resistance which causes an increase in blood insulin level and low blood glucose levels and this effect is called diabetogenic.
- Indirect effects of growth hormone: GH stimulates certain tissues like Liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, bones which in turn produces Somatomedin C (Insulin-like growth factor 1 which promotes cellular metabolism and prevents cell death and help cells divide and differentiate throughout the body.
Main causes are :
- Pituitary adenoma (tumor) – benign tumor of somatotropin cells in the anterior pituitary gland
- Hypothalamic tumors.
- Congenital disorders like – MEN 1( Multiple endocrine neoplasia TYPE 1 syndrome) /Wermers syndrome
- It is also associated with Macroglossia and Macrognathia
- Hyperpituitarism
SYMPTOMS:
- The growth of the hands, feet and lower jaw.
- Protrusion of the forehead
- Increased size of organs
- Excess sweating
- Temporal headaches
- Photophobia
- Reduction in vision
- The lips become thick and negroid
- The ribs also increase in size.
- Enlargement of the tongue.
DIAGNOSIS:
- IGF TEST -Elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 and GH In spite of receiving a large dose of glucose.
- MRI –It can help in confirming the presence of a pituitary tumor.
- X-ray- Enlarged Sella tursica, enlarged paranasal sinus, tufted terminal phalanges and widened carpal joint spaces.
- BLOOD TESTS: Oral Glucose tolerance test and hyperphosphatemia.
TREATMENT:
The aim is to reduce GH and IGF-1 production to normal levels
- SURGERY – It is done to remove the pituitary adenoma which depends on the size of the tumor. Chances of recurrence are possible if the tumor is not removed completely.
- Radiation therapy: It is an alternative resort to surgery
- Drug therapy:
- Dopamine agonists –Drugs such as bromocriptine and cabergoline are used to inhibit the Growth hormone. They are taken orally twice daily but side effects such as constipation and dizziness come with it.
- Somatostatin analogs –ocreotide and lanreotide are available. They are injected under the skin subcutaneous route. Another long-lasting Sandostatin LAR Depot is injected once a month deeply into the muscle via the intramuscular route.
- Growth hormone receptor antagonist –Pegvisomant is taken in the form of daily injections.