Addisons Disease
Addison’s disease is also known as primary adrenocortical insufficiency in which adrenal glands produces insufficient amount of cortisol or aldosterone due to various underlying causes.
Depending on the site of lesion,it is divided into two types:
- Primary: The adrenals are involved; ACTH levelsare high due to feedback. Causes include Addison's disease and congenital or acquired enzymatic defect.
- Secondary: Either hypothalamus or pituitary is involved.ACTH production is less. Causes are either hypothalamic or pituitary disease(hypopituitarism) or exogenous administration of glucocorticoids. It may be acute (adrenal crisis) or chronic (Addison's disease).
It may be acute (adrenal crisis) or chronic (Addison’s disease)
PRIMARY ADRENOCORTICAL INSUFFICIENCY – ADDISON’S DISEASE
The disease is uncommon but is awell-recognized complication in patients with AIDS. Otherwise, it is commonly due to tuberculosis, fungal and cytomegalovirus infection. Autoimmune adrenalitis is the commonest cause of Addison’s disease. It is more common in females.
CAUSES:
COMMON CAUSE:
- Autoimmune
- Sporadic
- MEN type I, II
- Infections e.g.tuberculosis, fungal and viral infections (HIV)
- Bilateral adrenalectomy
RARE CAUSE:
- Metastatic tumours
- Amyloidosis
- Waterhouse Frederickson’s syndrome (Adrenal haemorrhage in meningococcal infection)
- Haemochromatosis
- Adrenal infarction
PATHOLOGICAL CAUSES:
- HYOPERFUSION OF KIDNEYS:
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Congestive heart failure
- Diuretic therapy
- RENAL ISCHAEMIA:
- Malignant hypertension
- Renal artery stenosis
- HIGH RENIN PRODUCTION BY JUXTA-MERULAR APPARATUS:
- Barter’s syndrome
SYMPTOMS:
All the three zones of adrenal cortex are involved to some extent in Addison’s disease. The clinical picture is a blend of:
- Glucocorticoids insufficiency: weight loss,malaise , anorexia , nausea and vomiting , weakness , diarrhoea , fatigue.
- Mineralocorticoid insufficiency: hypotension or low BP between 90-100mmHg.
- Loss of androgens: Sparse axillary and pubic hair in females.
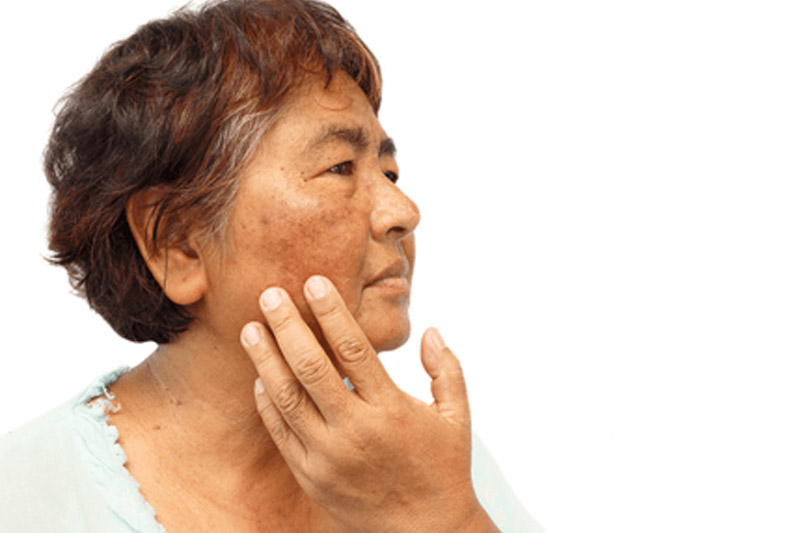
- Increased ACTH secretion: Pigmentation of sun exposed areas, elbow , knees , creases of palm , knuckles ,mucous membrane of mouth , scars etc. .Nipples and areolae to darken.
DIAGNOSIS:
- Basal plasma cortisol:
Morning – low and evening low. A random cortisol <100 nmol/L during the day is highly suggestive and >550 nmol/L makes the diagnostic unlikely
- Basal ACTH level:
Addison’s level – high
Pituitary or hypothalamus disease – low
- ACTH stimulation test (0.25 mg I.V. stat, blood sample at 30 mins and 60 min)
Plasma cortisol at 30 or 60 mins <1gug indicates Addison’s disease.
- Serum sodium is low.
- Serum potassium is high or normal.
- Blood glucose is low in severe disease.
- Plasma renin activity (PRA) is high.
- Aldosterone level – low in primary Addison’s disease, normal in secondary hypo adrenocorticalinsufficiency.
- Serum DHEA levels are low.
- Adrenal antibodies are present in autoimmune disease (50%)
- Chest and abdominal X-ray for tuberculosis and adrenal calcification.
MANAGEMENT:
The treatment is replacement therapy:
- GLUCORTICOID REPLACEMENT: oral prednisolone 20 mg in the morning and 10mg in the evening is the drug of choice .
- MINERALCORTICOID REPLACEMENT: fludrocortisone 0.05 mg/day is adequate to maintain BP, electrolyte and renin activity .
- ANDROGEN REPLACEMENT: replacement with adrenal androgen DHEA may be useful to some women with loss of libido
TREATMENT OF ADDISON’S DISEASE IN STRESSFUL CONDITION:
- Doses of prednisolone is doubled in the event of chronic illness.
- For minor surgery, hydrocortisone 100mg IM stat with premedication.
- For major surgery, injection hydrocortisone 100mg I.V 6 hourly for 24 hours, then half the dose is to be continued till stress is over.
COMPLICATION:
ADRENAL CRISIS: is defined as an acute precipitation of Addison’s disease under the effects of stress i.e., surgery, haemorrhage and infection. It is a medical emergency requires immediate treatment with corticosteroids (I.V hydrocortisone,mineralocorticoids,fluids , electrolytes and treatment of precipitating factors . Fluid replacement with normal saline /dextrose should be started immediately.