Aortic Valve Regurgitation
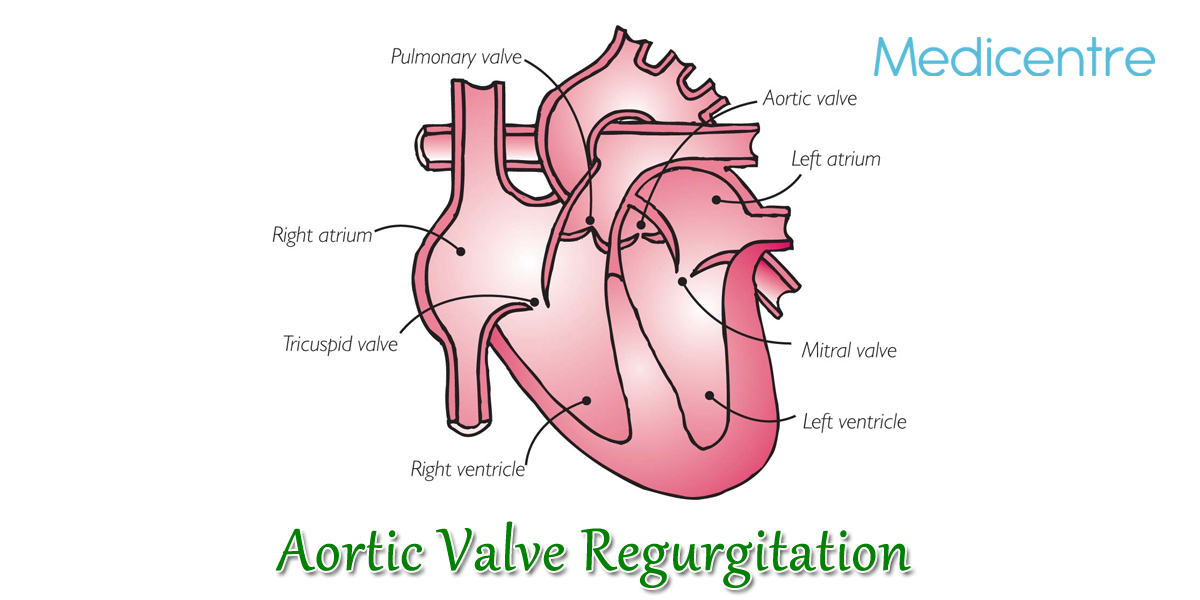
It is a clinical condition of the heart where the blood is pushed by the left ventricle into the aorta during systole, regurgitates back into it during diastole due to inadequate closure of the aortic valve leading to volume overload on the left ventricle, so with marked regurgitation means backflow of the blood, the stroke output of left ventricle is doubled and workload increases on the left ventricles and causes rise in left ventricle diastolic pressure after exercises which ultimately leads to rising in left atrial and pulmonary venous pressure producing congestion in lungs and dyspnoea . Aortic valve regurgitation can be acute -due to trauma or endocarditis that leads to rising to in left ventricular pressure and acute pulmonary edema. The chronic regurgitation -congenital or rheumatic develops slowly by leading to exertional dyspnoea, and then pulmonary congestion (cough, dyspnoea, hemoptysis).
It is a type of respiratory failure where the partial pressure of oxygen to the ratio of the fraction of inspired oxygen is less than 300mmHg. It causes inflammation in the lungs due to fluid accumulation in the lungs. It causes partial collapse of the lungs and low levels of oxygen in the blood
Causes OF Aortic Valve Regurgitation:
It has the following causes:
- CONGENITAL:
- Bicuspid valve
- ACQUIRED:
- Rheumatic heart disease.
- Infective endocarditis
- Trauma leading to valve rupture
- Marfan’s syndrome
- Syphilitic aortitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Dissecting aneurysms of ascending aorta
Symptoms OF Aortic Valve Regurgitation:
- Often asymptomatic
- Palpitation – pounding of heart
- Dyspnoea
- Orthopnoea
- Wide pulse pressure
- Dancing carotids
- Cyanosis
- Pitting ankle
- Tender hepatomegaly
- Head nodding with carotid pulse
- Bounding peripheral pulses
Diagnosis OF Aortic Valve Regurgitation:
- Electrocardiogram
- Chest x-ray
- Echocardiogram
- Colour doppler echocardiography
Treatment OF Aortic Valve Regurgitation:
- Underlying cause i.e. endocarditis , syphilis should be treated accordingly.
- Aortic valve replacement under cardiopulmonary bypass is quite effective in patients with moderate or severe aortic regurgitation with left ventricular enlargement due to overload like mechanical valves in younger patients and biological in older patients.
- Antibiotic prophylaxis is given to prevent endocarditis before and after surgery.