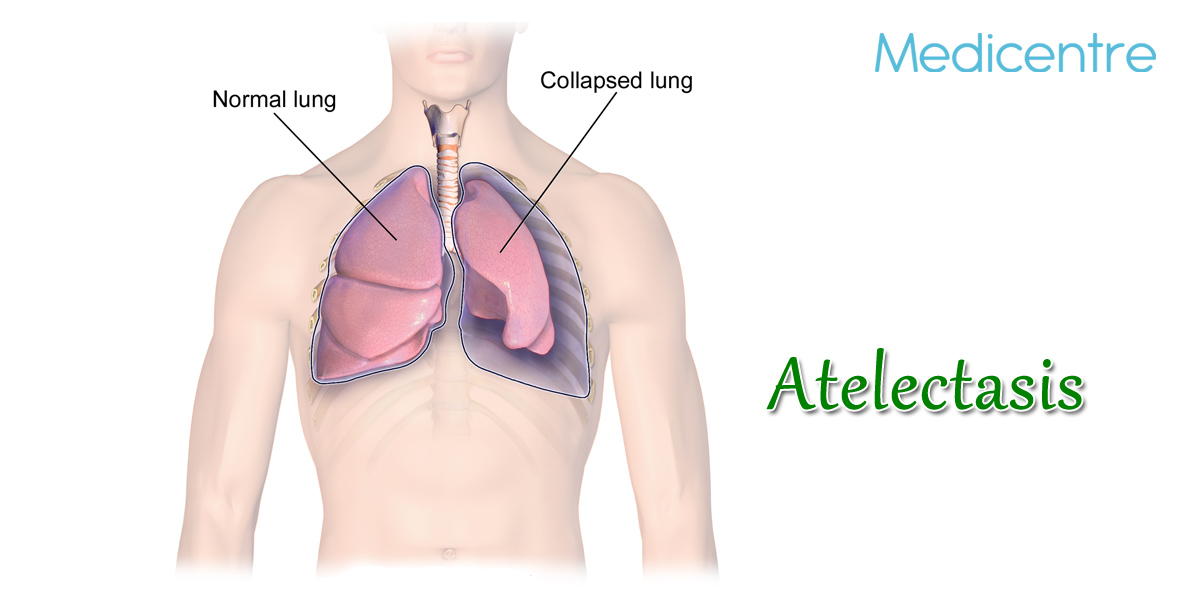
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is the medical condition where lobe of a lung or a lung collapses partially or completely. This medical condition is caused when the small air sacs in the lungs are reduced or deflated. Post surgery most of the patients complain for Atelectasis and it is the common breathing or respiratory issue that patients may experience after their surgical procedure. It can also be a possible complication for a variety of respiratory issues like inhaled foreign objects, cystic fibrosis, fluid in the lungs, lung tumours, chest injuries and serious asthma. The number of air sacs affected varies depending upon the cause and the symptoms and risk involved also vary. It needs to be addressed timely as it minimizes the oxygen intake. The treatment procedures are available and it is administered according to the severity and cause of Atelectasis.
Symptoms of Atelectasis:
There are basically no obvious symptoms, but patients may experience one or the other symptoms of Atelectasis mentioned below and this includes:
- Coughing
- Rapid and shallow breathing
- Dyspnea or difficulty in breathing
- Low grade fever
What Are the Causes of Atelectasis?
Atelectasis may sometime results from blocked airways or pressure from outside the lungs. There are some patients who experience Atelectasis because of anaesthesia administered to them during surgery. Anaesthesia make changes in the airflow dynamics within lungs and regulates the absorption of pressures and gases and all these cause damaging effects to the air sacs in lungs. It may be caused to patients who have undergone heart bypass surgery.
Blockage in the bronchial tubes may also cause obstructive Atelectasis and the possible causes of the blockage in air passage include:
- Mucus plug in the airways and it often occurs during or post surgery as the patients can’t cough out the mucus and hence Atelectasis is caused. The medications prescribed post surgery also inflate the lungs than normal and hence secretions are collected in airways.
- Inhaling Foreign objects which transfer into the lungs and may block the sacs
- Chronic infections like fungal infections, tuberculosis and other diseases can constrict or make scars in the major airways causing Atelectasis
- Blood clotting due to excessive bleeding in lung which you can’t cough out can also block the airways and air sacs
- Abnormal growth of tumours can also block the air sacs causing Atelectasis
Risk Factors of Atelectasis
The factors which can increase the risk of developing Atelectasis are:
- Premature growth of child where the lungs are not developed fully
- Lung diseases like bronchiesctasis, asthma and cystic fibrosis
- Conditions that interferes with the impulsive yawning, coughing and sighing
- Abnormal swallowing functions in adults
- Abdominal or chest surgery
- Confinement to your bed without any position changing
- Surgery under general anaesthesia
- Swallowing breathing resulting from rib fracture or abdominal pain
- Obesity
- Respiratory muscle weakness
Complications of Atelectasis include:
- Lung scarring which may be present even after the lung is inflated back again
- Atelectasis impact the lungs adversely and this reduces oxygen supply to air sacs
- Pneumonia may also develop until the Atelectasis is completed vanished. The mucus present in the air sacs can act as the breeding ground for the infections
- Failure of respiratory
Diagnosis of Atelectasis
Doctors usually ask to do a chest x-ray to diagnose Atelectasis. The x-ray is done to find out the cause of Atelectasis and to closely know the underlying cause of Atelectasis other tests are done including:
- CT Scan – This is the plain x-ray that is done to find out Atelectasis and it allows to measure the doctor the lung volumes in all and the other parts of lungs. It can also help the doctor to find out if any tumour is causing the collapse of lungs
- Ultrasound – It is done to find out the accumulation of fluid outside lungs which is compressing the lung tissue. It can also help doctors to remove the fluid accumulated
- Oximetry – This is the test which is done using a small device and it is done to measure the amount of oxygen saturation in blood
- Bronchoscopy – Performed with a flexible tube which is threaded down to throat and it enables the doctor to see and remove obstructions in airways
Treatments for Atelectasis
- Chest Physiotherapy – This is the therapy which help patients to breathe deeply after the chest surgery as it re-expand the lung tissues. Doctors will help you learn the techniques like coughing, clapping on chest to loosen mucus, performing some deep breathing experiences etc. Position the body so that the head is lower than chest and it is referred as postural drainage. Supplementing oxygen can also relieve the shortness in breathing.
- Medications – There are some medications which are prescribed and this include the inhaled bronchodilators that opens up the lungs to make breathing easier and smoother. Acetadote is prescribed to make mucus thin and make coughing easier. Pulmozyme is used for clearing the mucus plugs in cystic fibrosis.
- Surgery may also be prescribed by doctors to remove the airways obstructions and it is performed by suctioning all the mucus.